Services
Division of Paediatric Orthopaedics

Staff
- Dr. W Chow
- Prof. M To
- Dr. E Kuong
- Dr. N So
- Dr. J Wong
- Dr. C Lee
The division looks after all aspects of paediatric orthopaedics, which has changed dramatically in the recent two decades. Problems that were once prevalent, like tuberculosis and poliomyelitis, are now uncommon. Instead we now see a wide variety of diseases, none of which is prevalent except for developmental problems like flatfoot and intoeing. A holistic approach is practised in caring for these young individuals with orthopaedics problems. There are also significant advances in fields like computerised gait analysis in cerebral palsy, and limb lengthening and reconstruction, which demands constant service review and research.
In-patients are taken care of at The Duchess of Kent Children’s Hospital (DKCH) and Queen Mary Hospital, while out-patients are seen at DKCH. Specialist clinics cover neuromuscular, fracture, congenital hand, leg length discrepancy and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
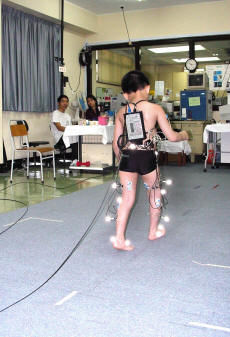
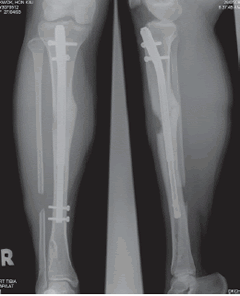
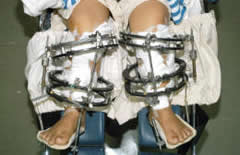
To keep pace with advances in paediatric orthopaedics, we have developed a gait analysis laboratory which is ‘ constantly upgraded with latest technology. We perform gait analysis for patients ranging from cerebral palsy, myelomeningocele and leg length inequality to cervical myelopathy. Our division also pioneered the use of selective dorsal rhizotomy and botulinum toxin injection for the treatment of cerebral palsy patients in Hong Kong. We also practise state-of-the-art limb lengthening surgery for patients with limb length discrepancy, limb deformity and dwarfism.
Research
Despite the relatively small size of the division and heavy clinical load, we feel that active pursuit of research is of vital importance in maintaining good clinical practice and advancing our understanding of paediatric musculoskeletal problems. Apart from the clinicians, our research effort is supported by an overseas fellow, postgraduate students and research assistants.
Examples of projects undertaken by the division
- Long term follow-up of remodelling in developmental dysplasia of the hip
- Results of subtalar fusion
- Scar formation and prevention in leg lengthening
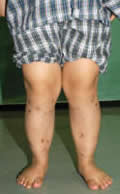
- Management of mobile flatfeet
- Hip arthrogram in cerebral palsy
- Epidemiology of paediatric fractures
- Cervical spine problems in Down’s syndrome
- Management of Clubfeet
- Assessment of dynamic ankle foot orthosis (DAFO) by computerized gait analysis
- Comparison of Botox injections vs casting in spastic cerebral palsy
Selected recent publications
- Li YH, Hafeez M, Emery RJ, Leong JCY: The c/b ratio in the radiological monitoring of the hip joint in congenital dislocation of the hip, J Pediatr Orthop. 1995 Nov-Dec;15(6):806-ll.
- Li Y.H., Leong J.C.Y; Fractured lateral epicondyle associated with lateral elbow instability, Injury, Vol 26, No. 4, 267-268, 1995
- Li Y.H., Chow W, Leong J.C.Y; The Sofeild-Millar Operation in Osteogenesis Imperfecta, a modified technique Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery(B),ll-16, 82(B), 1, 2000.
- Fong H.C., Lu W.W., Li Y.H. and Leong J.C.Y., Chiari; Osteotomy and shelf augmentation in the treatment of hip dysplasia, Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2000, 20: 740-744.
- Legaspi J, Li YH, Chow W, Leong JC: Talectomy in patients with recurrent deformity in club foot. A long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001 Apr;83(3):384-7.
- Yau P.W.P., Chow W., Li Y.H. and Leong J.C.Y.: Twenty-Year Follow-up of Hip Problems in Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita, Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2002, 22(3): 359-363.
- David Ip, Y.H. Li, W Chow, JCY Leong; Reconstruction of forearm deformities in multiple cartilaginous exostosis. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics (B) 2003, 12:17-21